|
risks.
As regards prior use data, once again the site and
duration of exposure of the new device compared to the
prior use should be kept in mind. These data provide
either an estimate of risk in line with Clause 4.4 of
EN/ISO 14971 or a measure of the acceptability of
risks in line with Clause 4.5, respectively.
Acceptable results from appropriate biological tests,
of the sort described in the EN/ISO 10993 series of
standards, may give a degree of reassurance that the
risk of adverse reactions occurring during clinical
use is low. EN/ISO 10993-1 indicates evaluation tests
which can form a framework for the development of an
assessment programme. These tests, commonly termed
biocompatibility tests, differ from basic toxicity
tests in that they typically attempt to mimic the
conditions of clinical exposure to medical devices and
thus provide an indication of the probability of
adverse effects arising during use. They tend, as a
result, to be less sensitive than basic toxicity tests
and are thus a less discriminating indicator of risk.
Biocompatibility test data should therefore be used to
complement an assessment based on materials
characterisation, rather than as a replacement for it.
It may
not be necessary to perform tests suggested by the
standard in all cases. Where the proposed materials
have already been extensively used or tested, little
or no biological testing may be necessary to judge the
biological safety of the device. Conversely, the need
for additional tests such as mutagenicity or
metabolism studies should be considered on a case by
case basis. National laws may prohibit unnecessary
animal tests and the need for testing should always be
judged in relation to the predictive value of the test
and animal welfare considerations.
At GLR we offer
comprehensive program of biological safety
assessments, literature search, identify data gaps and
biocompatibility testing. Our scientists have
extensive experience in risk assessment and safety
evaluation of all classes of medical device and can
offer expert advice on how to go about testing of
medical devices.
We are providing some
basic information on biocompatibility ie.,
classification of medical devices. These information
will be very useful when placing biocompatibility
tests. Please feel free to contact us if you have any
questions.
|
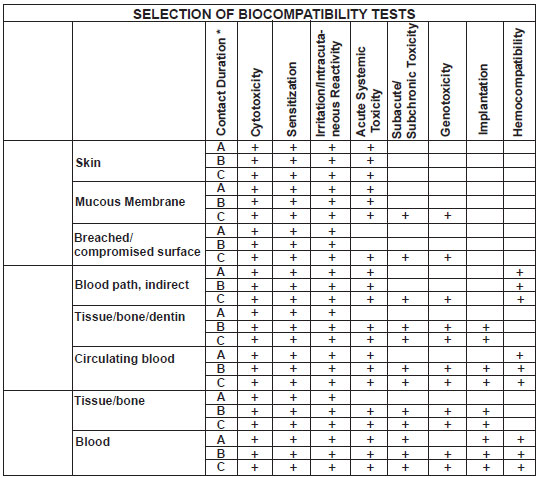
CLASSIFICATION OF
DEVICE BASED ON SITE OF CONTACT |
|
Surface Device |
Skin |
Gloves, ECG
electrodes, Adhesive tapes, Bandages and Monitors. |
|
Mucous membrane |
Contact lenses,
Catheters, Sigmoidoscope, Colonoscope, Gastroscope,
Endotracheal tubes, Bronchoscopes, some dental
prostheses, some Orthodontic devices, Condoms and
IUD’S. |
|
Breached or
Compromised Surfaces |
Wound care treatments
for ulcer, burn and granulation tissue Dressings
or Healing devices and Occlusive patches. |
|
External Communicating
Device |
Blood path indirect |
IV sets, Blood
administration sets, accessory tubings,
Hemodialysis tubings. |
|
Tissue/ Bone/ Dentin
Communicating |
Laparoscopes,
Arthroscopes, Draining systems, Dental cements,
Dental filling materials, Skin staples. This
category also includes devices which contact
internal tissues (rather than blood contact
devices). Surgical instruments and accessories. |
|
Circulating Blood |
Intravascular
catheters, Temporary pacemaker electrodes,
Oxygenators, Extracorporeal oxygenator tubing and
accessories, Hemoadsorbents and Immunoabsorbents. |
|
Implant Device |
Tissue/ Bone |
Intraocular lens,
Orthopedic pins, plates, screws and accessories,
Replacement joints, Bone prostheses, Cements and
Intraosseous devices, Pacemakers, Drug supply
devices, Neuromuscular sensors and stimulators,
Replacement tendons, Breast implants, Artificial
larynxes, Subperiosteal implants, Ligation clips. |
|
Blood |
Cardiac stents,
Pacemaker electrodes, Artificial arteriovenous
fistulae, Heart valves, Vascular grafts and stents,
Internal drug delivery catheters, and Ventricular
assist devices. |
|
CLASSIFICATION OF
DEVICE BASED ON DURATION OF CONTACT |
|
Classification |
Duration Of Contact |
|
A |
Less than 24 hours |
|
B |
1 day to 30 days |
|
C |
More than 30 days |
.
|
