|
Effect
Of Barium Sulphate As A Filler In Thermoplastic Polymer
For Medical Applications
Barium Sulfate as a filler
for composite preparation
Barium sulfate (BaSO4) is a
radiopaque material and filler used with medical-grade
polymers. Its specific gravity is 4.5. It is generally
used at loadings of 20 to 40% by weight. While a 20%
barium sulfate compound is typical for general-purpose
medical device applications, with striped tubing, for
example, a 40% compound is standard. As the barium content
increases, compounds begin to show losses of the base
polymer’s tensile strength and other mechanical
properties. It is therefore best to formulate radio
pacifiers at the minimum level for each application and
excessive use of these fillers is not recommended.
Method of composite
preparation
The barium sulfate is predried
before compounding. Thermoplastic polymers/BaSo4
composites are prepared using twin screw extruders with
increasing wt% loadings of barium sulphate. The material
coming through die is granulated after cooling through a
cooling bath. The granules are injection molded for
specimen preparation and testing. After testing the
results are studied and compared to decide application
areas. Once the required results are obtained the granules
of composites can be moulded or extruded to form end
products.
X-ray image of different
loadings with increasing wt% of Barium sulphate in
thermoplastic polymer Applications
 |
 |
|
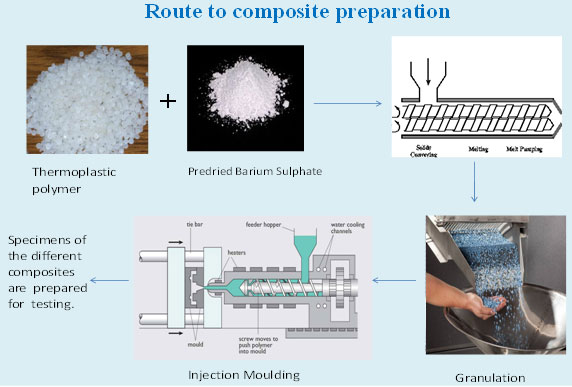
Dj stent (Used to bypass
kidney stone, temporarily after lithotripsy) |
Intravenous catheter (Used
to give fluids, drugs and for taking frequent blood
samples |
 |
 |
|
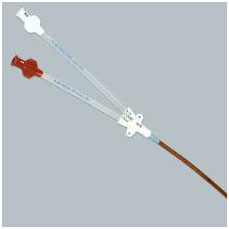
Endotracheal tube (Used to
ventilate, comatose or seriously ill patient) |
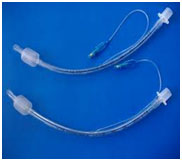
Drainage tubes (Used to
drain body fluids after surgery or in some diseases) |
 |
|
|
Ryle’s tube (Used to give
drugs or food directly to the stomach) |
|
Medical devices used for
diagnostic and other interventional procedures require the
device to be clearly visible under X-ray. Radiopacity is
highly required in medical applications in use of devices
such as catheters, tubing’s, swabs, wires, body implants
and dental products. This is because these devices are
inserted inside the human body and need to be tracked
properly while its insertion and removal. Toys can be made
radiopaque so that if they are accidently swallowed by
children they can be quickly detected in X-rays.
References
-
Plastics in Medical Devices-
Properties Requirements and Applications by Vinny Sastri.
-
Robert A Baker and J.M.Huber,
“An over View Of The Hidden Minerals Of Polymer
Applications”, Polymers, Laminations and Coatings
Conference, 1997, 17-28.
-
Additives for Plastics
Handbook by John Murphy.
-
Functional Fillers for
Plastics, Edited by Marino Xanthos, Second Edition, Wiley
VCH.
-
Mallick P.K, Fiber-Reinforced
Composites Materials-Manufacturing and Design, 3rd Edn,
Boca Raton Publishing, 1993.
-
Quiyun Peng,” Radiopaque
Medical Devices Containing Bismuth Oxychloride” EMD
Chemicals Inc., An affiliate of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt,
Germany, Hawthrone, New York 10532.
-
Guangyu Lu et. Al.,” Rheology
And Processing of BaSo4-filled Medical Grade Thermoplastic
Polyurethane”, Polymer Engineering & Science, Oct.
2004,Vol.44,No.10, 1941-1948.
-
www.lubrizol.com
-
www.fostercomp.com
Page
1 :
2 :
3 :
4 :
5 :
6 :
7 |
