|
Global
Trends in Medical Plastics Technology and Applications
The majority of medical devices are made
to be implantable systems. These devices are implanted
inside the human body and perform critical functions
either in the area of drug delivery or regulation of some
bodily function. Plastics form the core of many of these
devices, and the properties of the plastic material allow
greater functionality of the device.
The implantable devices are further
divided into short term implantable and long term
implantable devices depending on the duration of the dwell
time of the implantable device inside the body. Most
devices shorter than a 90 day dwell time are classified as
being short-term implants. Biological stability becomes an
important consideration for long term implantables.
Selection and Evaluation of Plastics
The selection of plastic materials is
clearly based on the properties of the material. The first
criterion is the physical properties of the material. This
is primarily based on the application and the requirements
of the device.
Once a material is chosen based on the
physical properties of the material, several other
material properties allow for the evaluation of
suitability of a particular material.
Thermal Properties: The behavior of the
material in thermal environments is of interest. This is
particularly relevant during sterilization of medical
devices. The process of sterilization can be done under
different conditions, usually at higher temperatures or
with exposure to high energy radiation. The ability of the
medical device material of construction to withstand these
conditions is big factor in deciding the suitability of a
material.
Chemical Resistance: The application of
the device will determine the type and the frequency of
contact with any chemical. The chemical may either be a
medicinal fluid or a bodily fluid. The higher the
resistance of the material to those chemicals, the greater
will be the efficiency and longevity of the device.
Electrical Properties: Plastics are in
general good electrical insulators; however, there may be
differences in the specifics of their dielectric constant
and breakdown voltages. Devices such as implantable
cardioverter defibrillators (ICD) carry high voltages and
depend on the surrounding insulation to withstand that
level of voltage. Measurement of the electrical properties
of a plastic material constitutes an important part of the
overall characterization.
Polymer Composition: Very often additives
such as anti-oxidants, ultra-violet protectors,
plasticizers etc. are mixed into a plastic to enhance
their performance. These additives, however, may not be
compatible with body contact and this has to be carefully
assessed before selecting a plastic. The extent of elution
of the additives can be assessed by doing an extraction
test in both polar and non-polar solvents. The extraction
test conditions and solvents are clarified in the Internal
Organization for Standardization (ISO) testing procedures,
specifically ISO10993.
Additive packages most frequently used in
medical applications are radiopaque additives such as
Barium sulfate. These radiopaque materials do not allow
x-rays to pass through them and they, therefore, are
clearly visible in x-rays making them very useful in
correct placement of devices.
The addition of most packages into
polymers is done using twin screw extruders. Twin screw
extruders with their variable screw geometry aids mixing
and are effective compounders.
Biocompatibility and Biostability :
ISO 10993 also details out the protocol for the
determination of the biocompatibility of a plastics. The
series of toxicity tests, as given in the standards,
clarifies the short term toxicity issues as well as the
long term genetic issues resulting from the material.
Quite often, the plastics material manufacturer also has
this information in their product datasheets.
Another aspect that is important in long
term implantable applications is the biological stability
of the material, often referred to as the biostability of
the material. When a device is implanted into the human
body, the implantation of a biomaterial elicits an
immediate response from the immune system of the human
body. This immediate response is intended to attack,
destroy or isolate the foreign body as the body sees the
implanted device as a foreign body. Monocytes, from the
body’s white blood cells (WBC) also migrate to the site of
inflammation and rapidly differentiate into macrophages.
When macrophages encounter a foreign objectthat is too
large to be phagocytosed, such as an implant, they adhere
and fuse to form larger foreign body giant cells (FBGCs)
in what is termed ‘frustrated phagocytosis.’ Clinical
observations indicate that these adherent cells may
persist at the tissue/implant interface for the lifetime
of the implant. During frustrated phagocytosis, adherent
macrophages and FBGCs form a closed compartment between
the cell and the biomaterial that facilitates the
generation of high local concentrations of reactive oxygen
intermediates (ROIs), acids and enzymes at the cell
/polymer interface. This is indicated in Figure 1
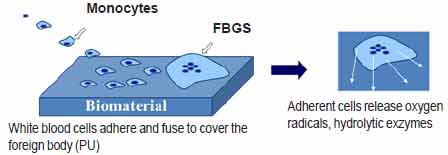
.Figure 1: Depiction of the body
response to the implantation of a biomaterial
|
